WordPress vs TYPO3 vs Craft CMS
In this article, we compare WordPress, TYPO3, and Craft CMS - platforms that allow you to manage and customize your website. We help you decide which CMS is the most suitable for your business and use case.
Bozidar
WordPress, TYPO3, and Craft are Content Management Systems(CMS). CMS helps you create manage, and organize content on your website, allowing you to easily add, edit, and delete text, images, videos, and other elements on your website. With a CMS you don’t have to manually code each webpage or update content directly in the website’s code. Instead, you use a simple dashboard or editor to make changes, and the CMS takes care of the rest, automatically updating your site’s design and layout. CMS platforms come with various features and functionalities that offer flexibility and different website needs.
Overview
WordPress
WordPress is an open-source, user-friendly CMS made for blogging. WordPress boasts a simple and intuitive interface, making it accessible to users with limited technical expertise. It offers an extensive library of themes and plugins, allowing users to customize their websites without the need for extensive coding knowledge.
TYPO3
TYPO3 is an enterprise-level CMS known for its robustness, scalability, and flexibility. It provides a comprehensive set of features, making it suitable for large-scale websites and complex web applications. TYPO3 offers advanced content management capabilities, including powerful workflow management, sophisticated access control, and multilingual support. It is highly customizable, allowing developers to create tailored solutions for specific business requirements. It’s built for more experienced users with coding expertise.
Craft
Craft emerged as a solution that was intended from the start to be an advanced and flexible content management system (CMS), a popular alternative to WordPress. The system is built on a foundation in the form of a PHP framework called Yii, mostly focused on technically experienced users because it comes without themes or blocks.
Ease of Use
Looking from a technical perspective WordPress was designed with beginners in mind, earning it a reputation for user-friendliness over the years. Users don’t need coding knowledge or previous experience to create a website. It offers a simple easy-to-use interface, an intuitive content management system with a block-based editor, and an extensive theme & plugin library. Due to its popularity, it has very large community support.
TYPO3 on the other hand has a steeper learning curve because out of the box it comes with more features and advanced functionalities. User interface is much more complex, so you may need some technical expertise to navigate efficiently. It also comes with an intuitive content management system that uses a block-based editor.
CraftCMS like TYPO3 isn’t tailored for users with no programming experience. It offers a relatively straightforward learning curve, with an intuitive interface for content creators.
Developers may need some familiarity with its structure for optimal usage because it comes without themes and with a very simple editor that offers almost no blocks.

Themes & templates
Themes & templates offer the visual appearance and functionality of a website. By changing the theme user can easily update the appearance of the content. Both TYPO3 and WordPress come with preinstalled themes, unlike Craft which after installation comes without any themes or templates so users need some programming experience to build their themes.
WordPress by default doesn’t use any templating engine, just a mixture of HTML and PHP code.
Craft CMS uses Twig templating language for PHP while TYPO3 uses a Fluid Template Engine.
Due to its popularity, WordPress has a large collection of free and premium themes and predesigned templates with different customization options. Looking at theme forest there are more than 10000 offered themes and templates. TYPO3 also offers a wide range of templates, but the selection may not be as extensive as WordPress due to not being that popular.
Users with some programming knowledge can extend base themes by creating child themes. This feature can be done both in WordPress and TYPO3.
Editor experience
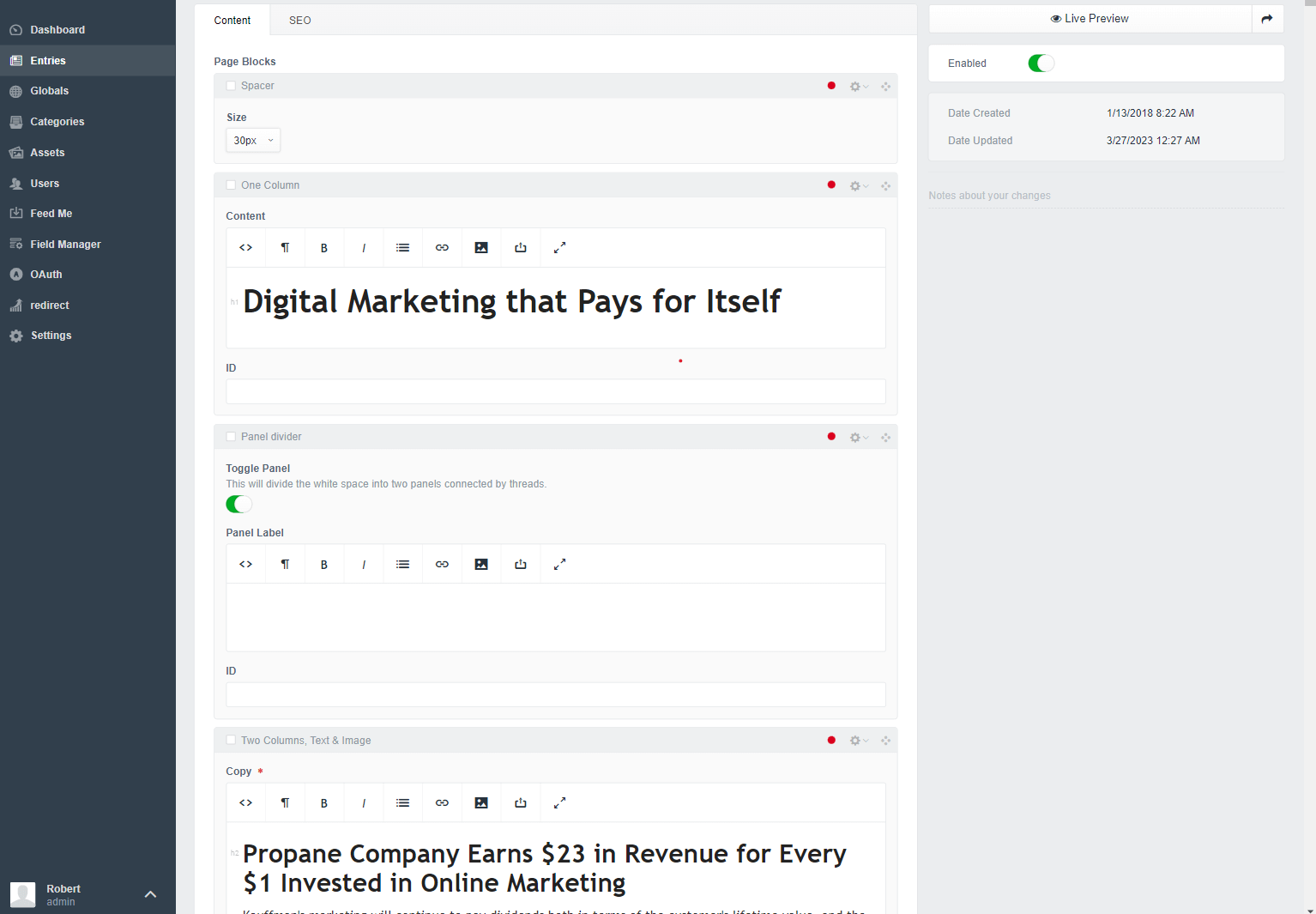
Through the page editor users can manage content, and add different blocks, elements, and lists to build the visual appearance of the page. WordPress uses a Gutenberg block editor that offers a full-page editing experience with a very modern UI. WordPress initially comes with over 40 blocks that have a wide variety of options and settings. Blocks can simply be dragged and dropped anywhere in the editor, and some blocks can be nested. It also provides block patterns that are predefined combinations of blocks. For more experienced users with the ACF plugin (Advanced custom fields), it is easy to extend blocks or create new ones.

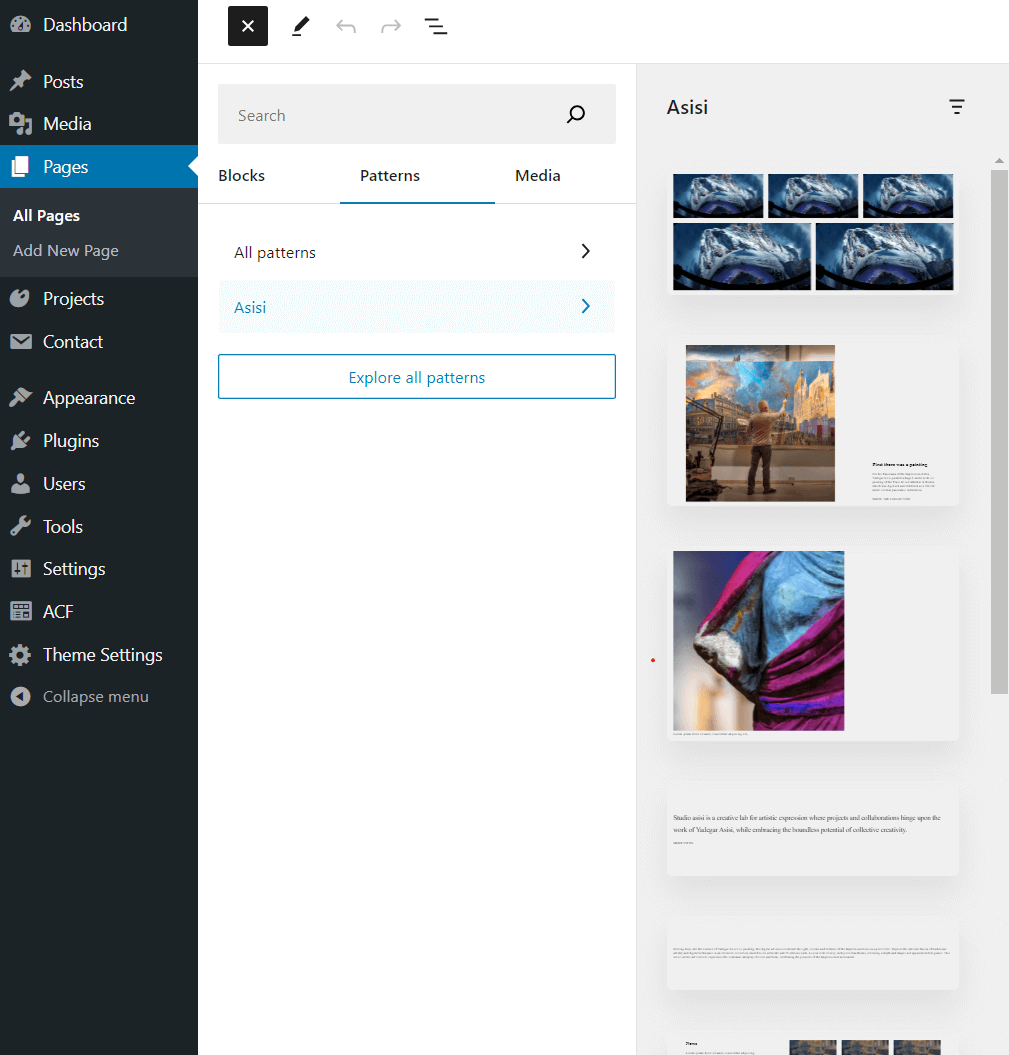
Craft out of the box comes with simpler UI, and no blocks, just field types. So users need to have programming skills to build blocks that will in the end be used in the editor.
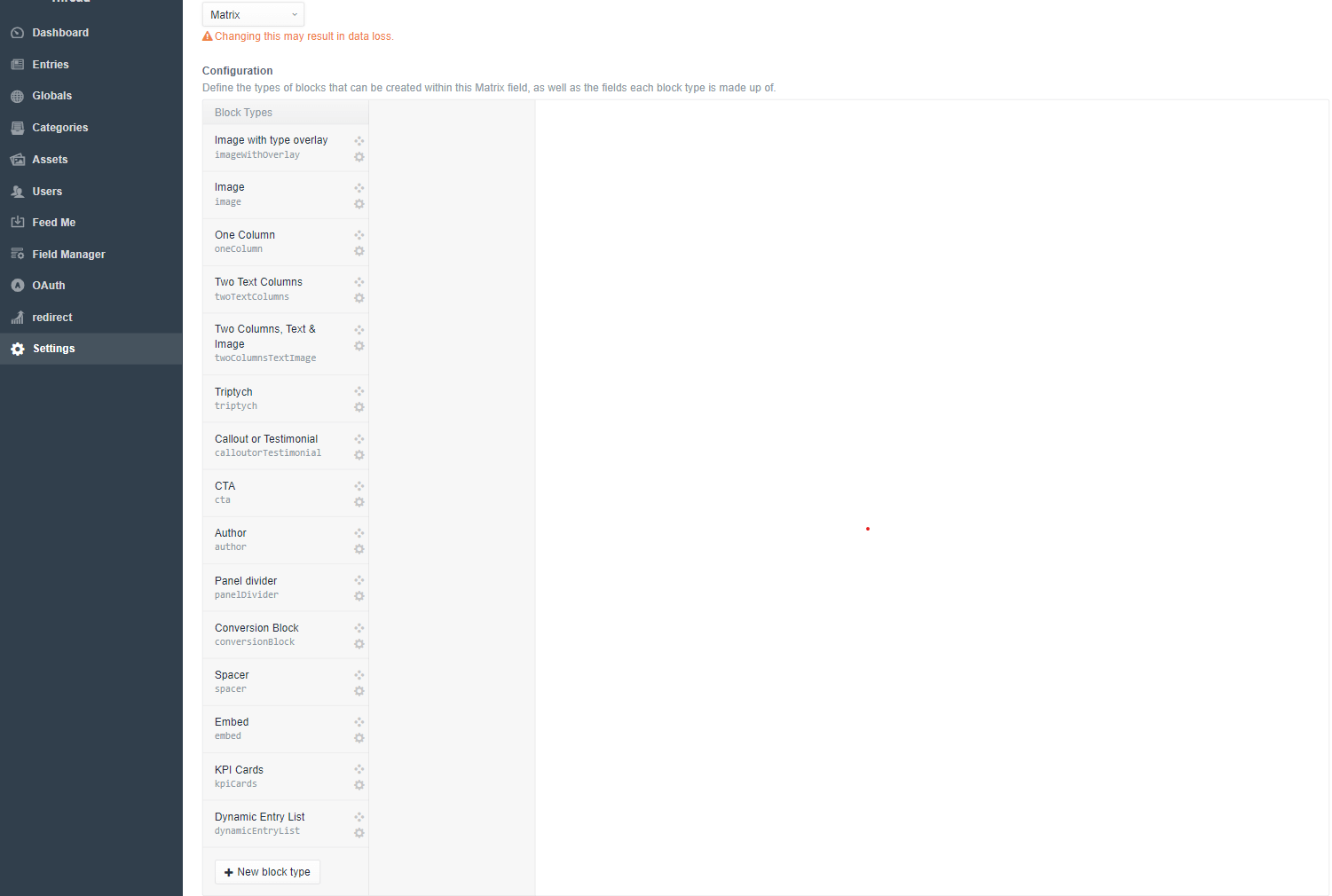
Craft offers matrix fields to easily build flexible pages by creating a collection of block types inside each matrix field.
In TYPO3 blocks are called content elements that are divided into few groups, like Wordpress comes with few of them out of the box. Editor has a simple UI, editing is a bit different then with Wordress and Craft because each block editing has its own page.
Blocks also offer lots of customization options, so programming skills are a must like in Craft when it comes to editing and block creation.
Plugins
Plugins/extensions are used to extend or add new functionality to CMS, ranging from simple solutions to more advanced ones. WordPress has an extensive plugin repository that offers more than 60000 plugins, free or premium ones. So, the big advantage is in this massive collection where you can find almost any functionality that you need, but also this is a drawback. Plugin code doesn’t have that strict quality control so they may degrade performance, often plugins become abandoned or don’t have regular updates which may cause site crashes or security vulnerabilities.

Craft also has a built-in repository, but the number is much smaller compared to WordPress due to its popularity. With a smaller repository code quality should be better, and regularly updated, and plugins can be installed and tested before purchase. The disadvantage of a much smaller plugin repository is that you are more likely to have to write the needed functionality yourself.

Typo3 plugins are called extensions, it has about 1000 extensions in its repository. Like with Craft, its smaller repository is an advantage. Extensions have better code quality and higher standards.
E-commerce
WordPress, Craft, and Typo3 offer e-commerce solutions. WordPress does so through a very popular free plugin called WooCommerce, Craft CMS has an e-commerce product called Craft Commerce and Typo3 has an e-commerce extension called Aimeos shop.
Unlike Craft and Typo3 which only offer a single solution WordPress as the most popular CMS has multiple e-commerce solutions but most of them are paid premium.
Community and support
WordPress has a massive community, endless guides, and plugins for almost anything. It’s easy to find help, both free and paid. TYPO3 has a smaller but loyal community, often tied to agencies and larger projects. Craft sits somewhere in between – fewer tutorials, but a solid Slack community and official support options if needed. For more complex builds, community size can be less important than having the right partner.
Performance and scaling
All three can handle speed and traffic well if set up right. TYPO3 is built for large, complex sites. Craft is light and clean, great for custom setups. WordPress can be very fast too, especially with caching and a well-optimized theme. The difference usually comes from how the site is built and hosted – not the CMS alone.
SEO features
Each CMS can deliver strong SEO results. WordPress has well-known plugins like Yoast or RankMath that cover everything from meta tags to sitemaps. TYPO3 and Craft take a more technical-first approach. They have built-in tools or extensions, but some features might require a developer to configure properly. Once set up, all three give full control over SEO.
Cost overview
WordPress is free, and you can do a lot with free plugins and themes. TYPO3 is also open-source but tends to require more development work upfront. Craft has a one-time license fee, plus optional plugins. In the long run, WordPress can be the cheapest to start with, but for bigger projects, costs level out. It depends on how much custom work is needed and how much can be reused from existing tools.
Still not sure which CMS is suitable for your business and need help?
Book a no-obligation discovery call and let's find the perfect solution.
Conclusion
Each CMS has unique strengths and serves different purposes, meeting different user needs:
WordPress: This CMS shines in its affordability and broad feature set, making it ideal for smaller businesses, blogs, or informational websites that require minimal technical expertise. An extensive library of plugins and themes allows for significant customization, but users should be wary of compatibility and quality issues when integrating third-party plugins.
TYPO3: Known for its robustness and flexibility, TYPO3 is tailored for enterprise-level projects. It is suitable for large corporations and organizations that need secure, scalable solutions with advanced workflow management. However, the steeper learning curve and complex features require technical expertise to use effectively.
Craft CMS: Built for tech-savvy users, Craft CMS is designed for projects that require complete control over content and appearance. It is suitable for creative agencies or companies with unique branding needs. The simplified architecture facilitates sophisticated customization but requires advanced programming skills.


